A Single Pole Double Throw Switch is an electromechanical device that can direct current to one of two paths. It has three terminals: one common terminal (C), and two output terminals usually referred to as normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC). When the switch is in the “open” position, the current flows from the common terminal to the NO terminal, and when it’s in the “closed” position, the current flows from the common terminal to the NC terminal. The switch allows for a circuit to be redirected from one output to another, making it useful for applications where alternating between two circuits is necessary, such as switching between different sets of lights or devices within an electrical system.
The Single Pole Double Throw Switch has only two terminals. The middle terminal is the input terminal(common terminal), and the terminal on the left or right is the output terminal.
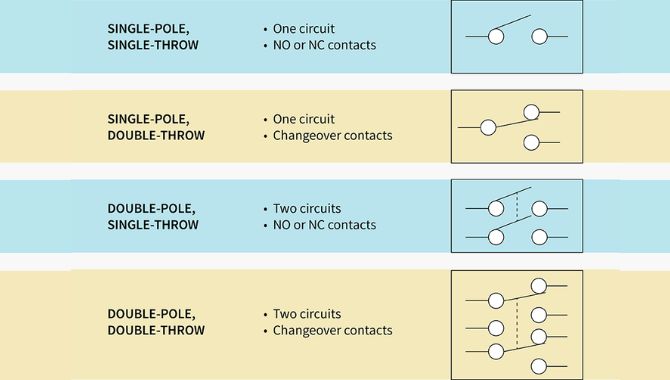
what are poles and throws?
The conventional wiring method is as follows: connect the live wire or the positive terminal to the middle input terminal, and connect the output terminal to one terminal of the device. Finally, connect the other terminal of the device with the other end of the input terminal to the power supply.
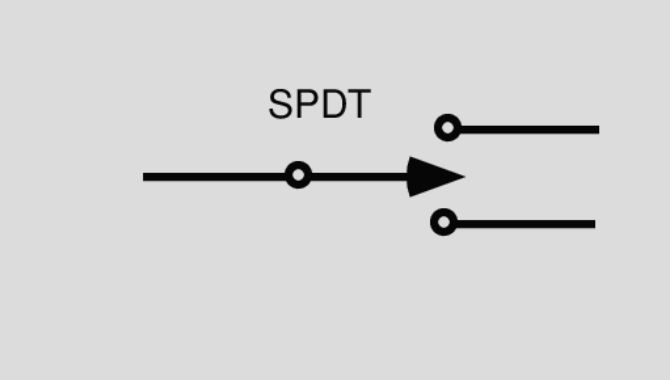
Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) Switch Electrical Circuit
Here is an example of a circuit diagram for a single-pole single-throw switch controlling a light bulb.
At the same time, you can replace the above light bulb with your corresponding device.
Application areas of different voltages
The voltage of the switch is divided into DC switch and AC switch. Different voltages have different application fields. Below I will specifically introduce the application of different voltages.
| Voltage | Application |
| 12V | Automotive Electrical Systems UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) Solar Power Systems LED Lighting Portable Electronics |
| 24V | Automotive and Truck Applications Power Tools and Equipment Small Electric Vehicles Industrial Automation Equipment |
| 36V | Electric Bicycles and Scooters Power Tools Small Electric Vehicles |
| 48V | Electric Bicycles and Scooters Electric Vehicles (Light) Energy Storage Systems Power Tools |
| 110V-120V | Residential Power Systems Electronics Power Tools |
| 220V-240V | C ommercial Power Supply |
What are the conventional currents?
| Electric current | Application |
| 0.1A-1A | Tiny electrical flows, often used in low-power devices. |
| 6A | Mid-range currents suitable for more demanding consumer and automotive applications. |
| 10A-16A | Electric bicycles, scooters, higher-powered tools, residential appliances. |
| 20A | Energy storage systems, light EVs, larger power tools. |
| 30A | Small residential power systems, heavy-duty tools, and electronics. |
| 40A | Industrial equipment, HVAC systems, commercial appliances. |
Summary of Applications:
| Configuration | Applications |
|---|---|
| ON OFF | Ligh |
| ON ON | Circuit selecti |
| ON OFF ON | Fan spee |
| (ON) OFF ON | Vehicle |
| (ON) OFF (ON) | Motor direc |
Features
After selecting the voltage, you can choose the specific switch type for your application.




 Toggle Switch
Toggle Switch


