MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) Detailed Explanation and Analysis of Customer Focus Points
I. Basic Overview of MCB
MCB, short for Miniature Circuit Breaker, is an indispensable terminal protection device in building electrical terminal distribution equipment. Let’s delve into various aspects of MCB for you.
- Definition and Application
- MCB is the most commonly used protective device in building electrical terminal distribution, specifically designed to provide short-circuit, overload, and overvoltage protection for single-phase and three-phase circuits up to 125A.
- Thanks to its small size, lightweight, and reliable operation, MCB finds widespread applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.

Working Principle
- MCB works by precisely monitoring the current to achieve protection against short circuits and overloads.
- In the event of a short circuit, the MCB immediately cuts off the circuit, preventing potential safety hazards caused by excessive current.
- When an overload occurs, the MCB delays disconnecting the circuit for a certain period, protecting electrical equipment from damage.
- Additionally, the MCB features overvoltage protection, which can disconnect the circuit during voltage abnormalities to avoid equipment damage.

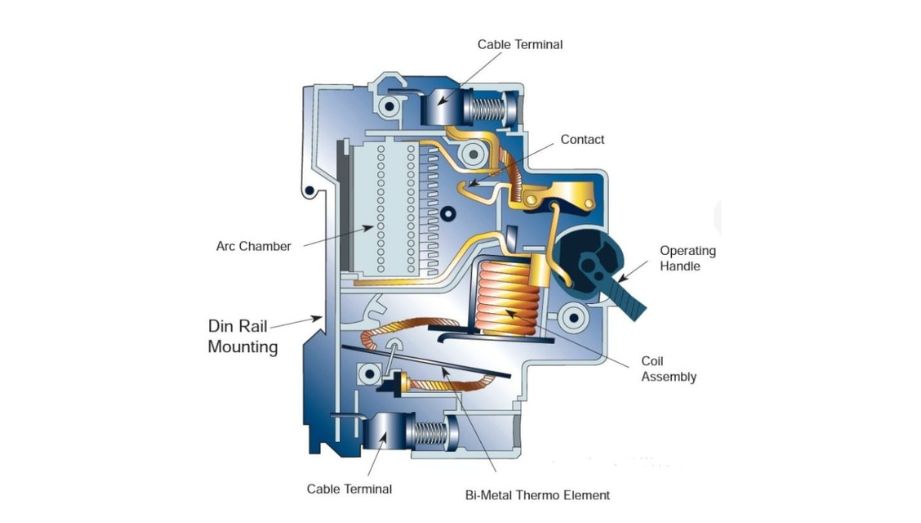
Structural Components
- The MCB primarily consists of the circuit breaker body, an electromagnetic tripping device, and a current protection device.
- The circuit breaker body bears the responsibility of disconnecting the circuit and protecting equipment.
- The electromagnetic tripping device detects short circuits and reacts swiftly to disconnect the circuit.
- The current protection device detects overload faults and disconnects the circuit when the current exceeds the set limit.
II. Key Points for Selecting and Using MCB
When selecting and using an MCB, there are several aspects you should pay special attention to:
Key Selection Points
- Rated Current: Choose an appropriate rated current range based on the circuit load.
- Rated Breaking Capacity: Ensure that the MCB can safely disconnect the maximum fault current according to the circuit demand.
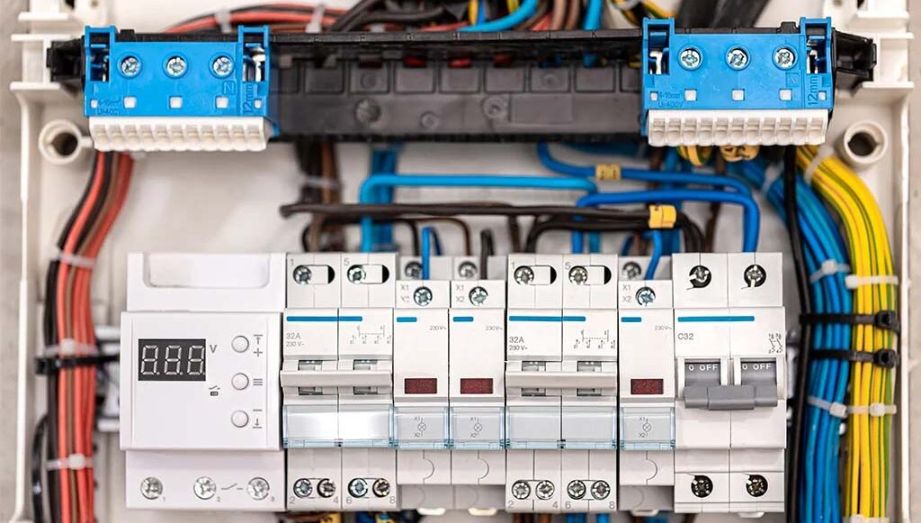
Installation and Usage Instructions
- Install the MCB in a distribution box or switch box to ensure circuit safety.
- Match the rated current of the MCB with the circuit load to avoid equipment damage or abnormal power outages due to overloads.
- Regularly check and test the working status of the MCB to ensure its normal operation.
- When repairing or replacing electrical equipment, always disconnect the corresponding MCB to prevent electric shock.
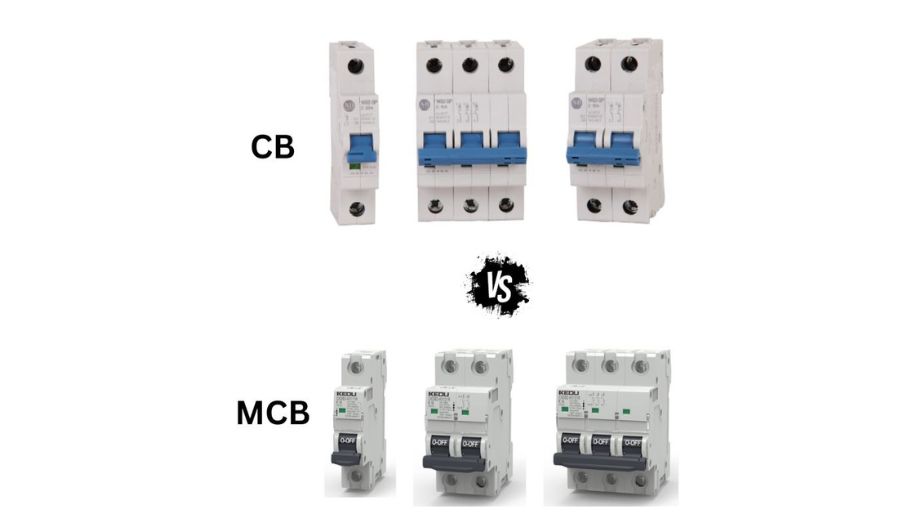
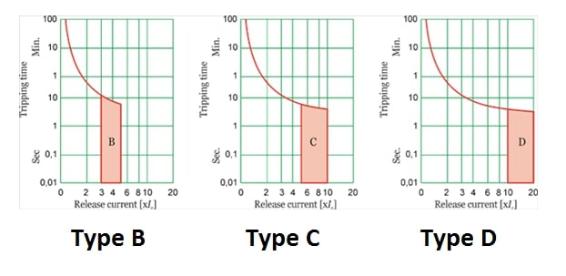
III. Types and Characteristic Analysis of MCB
- MCBs are classified into types B, C, and D based on their operating characteristics, designed to accommodate different electrical equipment needs.
- Additionally, MCBs come in various ratings such as 6A, 10A, 16A, etc., to meet the demands of different circuits.

IV. Key Focus Points for Customers When Purchasing MCB
When purchasing an MCB, customers typically consider the following core factors:
Safety and Reliability Evaluation
- Customers primarily focus on whether the MCB can quickly disconnect the power during circuit faults, preventing potential hazards.
- The speed and accuracy of the MCB’s action are crucial to the safe operation of the electrical system.
Selection of Rated Current and Breaking Capacity
- Customers choose an appropriate rated current based on the actual load conditions to ensure the MCB operates within its normal range without misoperation.
- They also consider the rated breaking capacity of the MCB to ensure it can safely disconnect the circuit during faults.
Consideration of Service Life and Maintenance
- The service life of the MCB is a significant aspect that customers value, preferring durable and stable products.
- Customers also consider the maintenance requirements and ease of the MCB.
Balance of Additional Functions and Protective Features
- Besides basic protective functions, customers may also be interested in whether the MCB offers additional features like leakage protection and overvoltage protection.
- These additional features provide customers with more comprehensive electrical protection, enhancing overall safety.

Consideration of Brand Reputation and After-sales Service
- Renowned brands often represent higher product quality and more reliable after-sales service, making them a preferred choice for customers.
- The quality and response speed of after-sales service are equally important, especially during equipment failures.

Evaluation of Price and Cost-effectiveness
- Price remains a significant aspect for customers. They comprehensively consider the product’s price, protective performance, and service life to evaluate its cost-effectiveness.
- Products with more reasonable prices, while maintaining performance and quality, are generally more attractive.
Application Fields of MCB
The usage scope of MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is extensive, primarily applied in the following areas:
Residential
: MCB serves as a crucial component in residential electrical systems, protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits. In households, various electrical appliances can cause excessive current, and MCBs can swiftly disconnect the power in such situations, preventing fires or equipment damage.

Commercial Buildings
: Commercial spaces like shopping centers and office buildings also widely use MCBs. These places often have complex electrical systems, where MCBs play a vital role in protecting circuits and ensuring the continuity and safety of commercial activities.

Industrial Facilities
: In industrial production environments, electrical equipment typically operates under heavy loads for extended periods. MCBs provide necessary circuit protection, preventing electrical accidents due to equipment failures or improper operations.

Public Facilities
: Public facilities such as hospitals, schools, and transportation infrastructure also rely on MCBs to ensure the stable operation of electrical systems. In these settings, the reliability of electrical systems is directly linked to public safety and service quality.
In summary, the usage scope of MCBs covers residential, commercial, industrial, and public facilities. Their significant role lies in protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits, thereby ensuring the safe and stable operation of electrical systems.